Digital Temperature Controller Digital temperature controller for heater cooler temperature controlling Professional Themostat Development,Digital Temperature Controller,Electric Temperature Controller,Seed Germination Thermostat Hellowave Technology Limited , https://www.hellowavetech.com
Analytical instruments thermogravimetric analyzers are mainly composed of balances, furnaces, temperature control systems, and recording systems.
Thermogravimetry is the most widely used and most widely used thermal analysis method. It is a technique for measuring the relationship between mass and temperature under programmed temperature control. Therefore, as long as the mass of the material changes when it is heated, the thermogravimetry method can be used to study its change process, such as dehydration, moisture absorption, decomposition, compounding, adsorption, desorption, sublimation, and the like. Thermogravimetry has been widely used in chemical and chemical related fields. The curve obtained by the thermogravimetry test is called the thermogravimetric curve (TG curve). The TG curve uses the mass as the ordinate, showing the mass reduction from top to bottom; the temperature (or time) as the abscissa, and the temperature from left to right ( Or time) increase. Thermoanalytical instruments are easy to operate, sensitive, fast, and require a small amount of sample, and the scientific information obtained is extensive.
The TGA experiment helps to study the changes of crystal properties, such as the physical phenomena of melting, evaporation, sublimation and adsorption; it also helps to study the chemical phenomena of substances such as dehydration, dissociation, oxidation and reduction. Thermogravimetric analysis can generally be divided into two categories: dynamic (heat up) and static (constant temperature).
Thermogravimetric analyzers (ie, thermobalances) for thermogravimetry are instruments that continuously record the relationship between mass and temperature. It is a combination of a furnace and a balance for mass and temperature measurement. The structure of the thermobalance is shown in the figure. 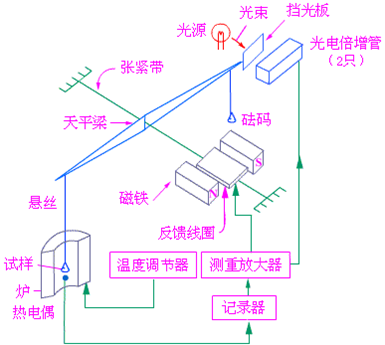
The main working principle of the thermobalance is to combine the circuit and the balance and to increase the temperature (or constant temperature) of the heating furnace at a certain heating rate through a program Temperature Controller. When the quality of the tested sample changes, the photoelectric sensor can convert the quality change into a direct current signal. This signal is amplified by the electronic amplifier and fed back to the moving coil of the balance, resulting in a reverse electromagnetic torque and resetting the balance beam. The potential difference formed by the feedback is proportional to the mass change (ie, it can be converted into a mass change of the sample). The change information is traced by a logger plotting the TG curve, as shown in Figure 2. This is a solid thermal decomposition thermogravimetric curve. The ordinate indicates the mass, and the abscissa indicates the temperature. The portion of the TG curve where the mass is essentially constant is called the platform, ab and cd in the figure, point b represents the starting point of the change, and the corresponding temperature Ti is the starting temperature of the change. The point c in the figure represents the end point of the change and Tf represents the end temperature of the change. From the thermogravimetric curves, data on the composition of the sample, the thermal decomposition temperature, and the like can be obtained.
Through the above introduction of analytical instrument thermogravimetric analyzer, I hope to help everyone work and study.
As a typical analytical instrument, the thermogravimetric analyzer has been widely used at present. In the following, we explain the working principle of the thermogravimetric analyzer.