Lipase, also known as glyceride hydrolase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides to produce diglycerides or mono-glycerides or glycerol and fatty acids. Crude lipases often have poor viability due to improper storage or long storage time. Therefore, crude lipase activity must be measured when used. There are many ways to detect lipase activity, and there are many substrates used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. So far, there has not been a unified detection method. Manufacturers and scientific research departments usually formulate their own detection methods according to their experimental conditions. The indexes reflecting the degree of lipolysis include acid value, iodine value, saponification value, and peroxide value. In this experiment, the acid value was used as an indicator, and 95% ethanol was used as a terminator. The determination of the acid value reflected the degree of decomposition of fat by lipase, and the enzyme activity was obtained. The aim is to explore a new rapid method for determining the activity of crude lipase.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental Materials
1.1.1 Eating Salad Oil: Commercially Available
1.1.2 Biological reagents
Crude lipase, standard lipase;
1.1.3 Chemical reagents
Phenolphthalein indicator 95% ethanol solution 0105 mol/L NaOH solution
1.1.4 Major Instruments and Equipment
Electric constant temperature water bath microtiter tube electronic balance SZF-06A fat fat analyzer Fiber Tester
1.2 Methods
1.2.1 Preparation of crude enzyme solution
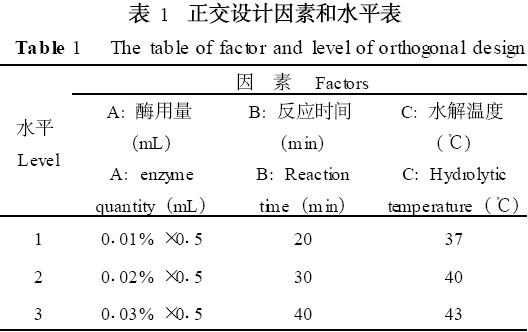
Weigh 0.010 g, 0.020 g, and 0.030 g of crude lipase with an electronic balance, dissolve and dilute to 100 mL with distilled water. Prepare crude enzyme solutions with concentrations of 0.01%, 0.02%, and 0.03%, respectively.
1.2.2 Experiment Design
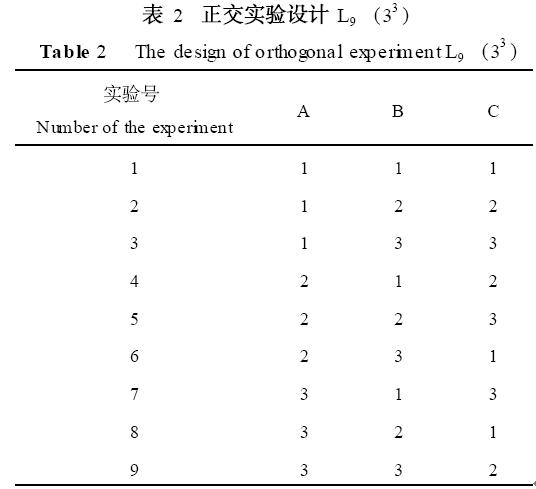
In this experiment, 10 mL salad oil was used as the substrate. The enzyme dosage, hydrolysis temperature, and reaction time were used as factors to determine the optimal conditions for hydrolysis by determining the acid value. Orthogonal experimental design is shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
1.2.3 Determination of acid value
The acid value refers to the number of milligrams of NaOH needed to neutralize 1 mol of free fatty acid, which is used to measure the degree of hydrolysis of the oil. In the experiment, the acid value of the hydrolyzate was determined by acid-base titration. According to the method used in the literature, 1 mL of 95% ethanol solution was added dropwise to the resulting hydrolyzate, and the reaction was terminated. Two drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added. Rapidly titrate with a solution of 0105 mol/L NaOH until the solution shows a reddish color and does not disappear within 30 s. Record the milliliters (V) of NaOH solution consumed. Blank values ​​were measured using the same method, and each test was repeated twice. The average value was used as the measurement result.
The acid value is calculated as follows:
X = C (V - V0) × 40 / M
Where: X - acid value of oil (mgNaOH / g oil)
C-NaOH standard solution concentration (mol/L)
M - Mass of sample (g)
40-mmol NaOH (mg/mmol)
1.2.4 Determination of crude lipase activity
Under the optimal hydrolysis conditions, the acid values ​​X1 and X2 of the crude lipase and the standard lipase hydrolyzate were measured, and the activity of the crude lipase was determined according to the formula U1 / U = X1 / X2, where U1 is the crude lipase activity. U is standard lipase activity.
1. 2. 5 Preparation of standard lipase solution
According to the best experimental conditions, prepare standard lipase solution.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Selection of optimal hydrolysis conditions
The test results are shown in Table 3.
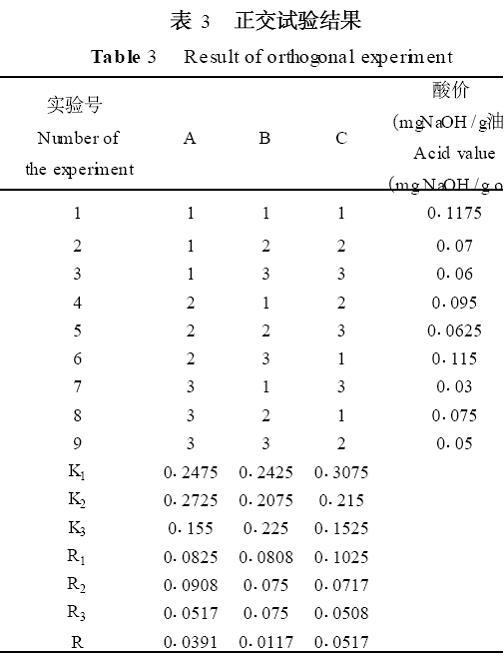
From the visual analysis in Table 3 (very poor analysis), that is, the value of R value can be seen, in the range of factors selected for the test, the order of the influence of each factor on the degree of hydrolysis is: hydrolysis temperature> enzyme dosage> reaction time; The optimal conditions for the test were C1A2B1, ie a hydrolysis temperature of 37°C, an enzyme dosage of 0102% and a reaction time of 20 min.
2.2 Determination of crude lipase activity
The X1 and X2 were measured to be 0.07 mg NaOH/g oil and 1.2675 mg NaOH/g oil respectively. The crude lipase activity calculated by substituting the formula was: 99.4 U/mg.
The crude lipase activity purchased was 100 U/mg. After being stored in the refrigerator for half a year, the enzyme activity decreased to some extent. The assay result was 99.4 U/mg, which was slightly lower than that of the original enzyme. This was due to a decrease in enzyme activity. Caused by, is a normal range, we can see that this method is feasible.
3 Conclusion
This method can be used for the determination of crude lipase activity, and the best enzymatic hydrolysis conditions are: enzyme dosage 0.02%, reaction time 20 min, hydrolysis temperature 37°C.
Fitness Mat
Padded Exercise Mat,Foldable Gym Mat,Fitness Matt,Workout Pads
Shenzhen Molding & Forming Industries Co.,ltd , https://www.mfi-cn.com