Bolts play a vital role in both manufacturing and construction industries. They are essential for assembling complex machinery like automobiles, bridges, and buildings due to their robust structure. These mechanical fasteners are indispensable for ensuring the integrity of assembled components.
Bolts function as external fasteners designed to pass through aligned holes in connected parts. Typically, they are tightened or loosened by turning a nut. Despite their varied shapes, most bolts share common characteristics, including a threaded cylindrical rod and a head at one end, often accompanied by a nut at the opposite end.
Table of Contents
- Sizes of All Types of Bolts
- Specifications of Hex Bolts
- Tolerances of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
- Head Types of High Tensile Bolts
- Flange Bolting Chart
- Advantages of SS Flange Bolts
- Components of an Eye Bolt
- Various Types of Eye Bolts & Applications
- Dimensional Standards of T-Head Bolts
- Tolerance Standards for Concrete of T-Head Bolts
- Types of J Bolts
- Applications of J Anchor Bolts
- Interior Uses of Hex Head Anchor Bolts
- Exterior Uses of Stainless Steel Anchor Bolts
- Test Certificates of Elevator Bolts
- Tensile Strength of Lag Bolts
- Tolerances on Length of Hanger Bolts
- Advantages of Plow Bolts
- Pros and Cons of Machine Bolts & Stud Bolts
- Strength and Durability of Arbor Bolts
- Properties of Blind Bolts
- Physical Properties of Low Carbon & Hot Dipped Galvanized Carriage Bolts
- Key Features of Rock Bolts
- Technical Specifications of Serrated Flange Bolts
- Differences Between Commercial Grade Shoulder Screws & Precision Shoulder Screws
- Head Types of Socket Head Bolts
- Applications & Uses of Square Bolts
- Surface Treatments of U Bolts
- Key Characteristics of Toggle Bolts
- Tensile Strength of Track Bolts

Sizes of All Types of Bolts
| Bolt Type |
Metric Size |
Imperial Size |
| Hex Bolt |
M5 – M56 |
1/4" – 2" |
| Anchor Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Elevator Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Eye Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Flange Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| J-Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Lag Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Hanger Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Plow Bolts |
M3-M60 |
1/2" – 3" |
| Machine Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Arbor Bolts |
M6-M20 |
1/2 to 5/8" |
| Blind Bolts |
M6-M16 |
1/2 to 5/16" |
| Carriage Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Rock Bolts |
M24-M36 |
1 to 1-1/2" |
| Serrated Flange Bolts |
M6-M20 |
1/2 to 5/8" |
| Shoulder Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
| Socket Head Bolts |
M3-M20 |
1/4 to 5/16" |
| Square Bolts |
M2-M160 |
3/8 to 8″ |
| T-Head Bolts |
M6-M16 |
1/4 to 5/8" |
| Tap Bolts |
M6-M24 |
1/2 to 5/16" |
| Toggle Bolts |
M4-M10 |
1/4 to 5/16" |
| Track Bolts |
M6-M20 |
1/2 to 5/16" |
| U-Bolts |
M10 to M100 |
3/8 to 8" |
Hex Bolts Are Recognized by Their Six-Sided Hexagonal Heads
Hex bolts, also referred to as hex head bolts or hexagonal bolts, are named for their unique head shape.
These bolts are a type of threaded fastener that can be either fully or partially threaded. They are versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction and machinery.
Their adaptability makes them ideal for various industrial applications. Hex bolts come in numerous sizes, materials, and finishes, providing users with the flexibility to select the best option for their specific application needs.
Specifications of Hex Bolts
- Metric Size: Diameter M5 – M56
- Lengths: 10mm – 800mm
- Imperial Size: Diameter 1/4" – 2" & Lengths 1/2" – 9-1/2"
- Threads: UNC, UNF, SAE, BSW
- Finishes: Zinc Yellow, Hot Dip Galvanized, Plain, Zinc Plated, Mechanical Galvanized, Stainless Steel
- Surface Treatment: Passivation, Plain
Tolerances of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
|
Nominal Screw Size |
Nominal Screw Length |
| Over 1 in. to2-1/2 in., incl. |
Up to 1in., incl. |
Over 4 in. to 6 in., incl. |
Over 2-1/2 in. to4 in., incl. |
Longer than 6 in. |
| 1/4 to 3/8 |
±0.02, -0.04 |
±0.02, -0.03 |
±0.06, -0.10 |
±0.04, -0.06 |
±0.10, -0.18 |
| 7/16 and 1/2 |
±0.02, -0.06 |
±0.02, -0.03 |
±0.08, -0.10 |
±0.06, -0.08 |
±0.12, -0.18 |
| 7/8 and 1 |
±0.02, -0.10 |
… |
±0.12, -0.16 |
±0.10, -0.14 |
±0.16, -0.20 |
| 9/16 to 3/4 |
±0.02, -0.08 |
±0.02, -0.03 |
±0.10, -0.10 |
±0.08, -0.10 |
±0.14, -0.18 |
Head Types of High Tensile Bolts
| Bolt Head Type |
Where It’s Used |
| Hex Head |
Building Structures and Machines |
| Socket Head |
Machines, Cars, |
| Flat Head |
Woodworking, or Any Application |
| Pan Head |
Electronics and Machinery |
| Round Head |
Decorative Purposes |
| Hexagon Socket Head |
Situations Where You Can’t Access the Back |
| Torx Head |
Automotive, Electronics |
| Slotted Head |
Where Less Torque is Required |
| Phillips Head |
General Purpose |
| Wing Head |
Furniture Assembly |
| Square Head |
Specific Applications |
| Dome Head |
Decorative or Prominent Parts |
| Knurled Head |
Manual Adjustments |

Flange Bolts Are Available for Class 150 to 1500 Flanges
Flange bolts are versatile fasteners widely used across multiple industries. Their distinct design allows for better weight distribution, making them ideal for applications requiring secure fastening.
They can be utilized for class 150 to 1500 flanges, particularly where resistance to high temperatures is necessary. Ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability of products is essential, and the following chart provides guidance on which class would suit your application needs.
Flange Bolting Chart
| Â |
Nominal Pipe Size (Inches) |
RF Height |
1/2 |
3/4 |
1 |
1 1/4 |
1 1/2 |
2 |
2 1/4 |
3 |
3 1/2 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
18 |
20 |
24 |
| Class150 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
16 |
20 |
20 |
| Diameter of Bolt |
 |
1/2 |
1/2 |
1/2 |
1/2 |
1/2 |
5/8 |
5/8 |
5/8 |
5/8 |
5/8 |
3/4 |
3/4 |
7/8 |
7/8 |
7/8 |
1 |
1 |
1 1/8 |
1 1/8 |
1 1/4 |
| Stud Bolt Length |
0.06 |
2 1/4 |
2 1/2 |
2 1/2 |
2 3/4 |
3 |
3 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 3/4 |
4 |
4 1/4 |
4 1/2 |
43/4 |
5 1/4 |
5 1/4 |
53/4 |
6 1/4 |
63/4 |
| Machine Bolt Length |
0.06 |
2 |
2 |
2 1/4 |
2 1/4 |
2 1/2 |
2 3/4 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 1/4 |
3 1/4 |
3 1/2 |
4 |
4 |
4 1/2 |
4 1/2 |
5 |
5 1/2 |
6 |
| Class300 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
16 |
20 |
20 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
| Stud Bolt Length |
0.06 |
2 1/2 |
3 |
3 |
3 1/4 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
4 |
4 1/4 |
4 1/4 |
4 1/2 |
43/4 |
43/4 |
5 1/2 |
6 1/4 |
63/4 |
7 |
7 1/2 |
73/4 |
8 |
9 |
| Machine Bolt Length |
0.06 |
2 1/4 |
2 1/2 |
2 1/2 |
2 3/2 |
3 |
3 |
3 1/4 |
3 1/2 |
3 3/4 |
3 3/4 |
4 1/4 |
41/4 |
43/4 |
5 1/2 |
53/4 |
6 1/4 |
6 1/2 |
6 3/4 |
7 1/4 |
8 |
| Class400 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
16 |
20 |
20 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
| Stud Bolt Length |
1/2 |
3 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 3/4 |
4 1/4 |
41/4 |
43/4 |
5 |
5 1/2 |
5 1/2 |
53/4 |
6 |
63/4 |
7 1/2 |
8 |
8 1/4 |
8 3/4 |
9 |
9 1/2 |
10 1/2 |
| Class600 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
24 |
24 |
| Stud Bolt Length |
1/2 |
3 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 3/4 |
4 1/4 |
4 1/4 |
43/4 |
5 |
5 1/2 |
53/4 |
6 1/2 |
63/4 |
7 1/2 |
8 1/2 |
03-Mar |
9 1/4 |
10 |
10 3/4 |
11 1/4 |
13 |
| Class900 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
| Raised Face 0.25 in. |
1/2 |
3 |
3 1/2 |
3 1/2 |
3 3/4 |
4 1/4 |
4 1/4 |
4 3/4 |
5.75 |
 |
6.75 |
7.5 |
7.5 |
8.75 |
9.25 |
10 |
10.75 |
11.25 |
12.75 |
13.75 |
17.25 |
| Class1500 |
Number of Bolts |
 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
| Raised Face 0.25 in. |
1/2 |
4.25 |
4.5 |
5 |
5 |
5.5 |
5.75 |
6.25 |
7 |
 |
7.75 |
9.75 |
10.25 |
11.5 |
13.25 |
14.75 |
16 |
17.5 |
19.5 |
21.25 |
24.25 |
Benefits of SS Flange Bolts
- Load Distribution
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity
- Simplified Assembly
- Cost-Effective
- Reduced Loosening
- Enhanced Aesthetics
Eye Bolts Are Primarily Used for Light-Duty Applications
Eye bolts are mainly used for light-duty applications since heavy loads can cause the eye to deform or even break. These bolts consist of a simple structure, featuring a threaded shaft and an eye at one end, typically secured with a nut. They are inserted into structures like wood or steel supports to provide a stable attachment point for ropes or cables during lifting operations.
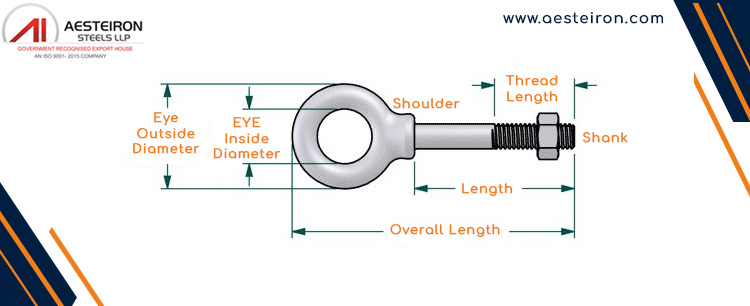
Components of an Eye Bolt
| Part |
Purpose |
| Eye |
For connecting hooks, ropes, and other attachments. |
| Shank |
Transfers the load by inserting into or through a substance. |
| Threaded Portion |
Ensures a tight fit when screwed into a tapped hole or nut. |
| Head |
Serves as a bearing surface to prevent the bolt from slipping out. |
| Shoulder |
Prevents the bolt from sinking too deep and distributes stress evenly. |
| Nut |
Secures the eye bolt in place, adding extra stability. |
Various Types of Eye Bolts & Applications
| Type of Eye Bolt |
Applications |
| Standard Eye Bolt |
Construction, Automotive, and Marine Applications |
| Shoulder Eye Bolt |
Used in Lifting and Rigging Operations |
| Heavy-Duty Eye Bolt |
Heavy Lifting and Industrial Applications |
| Swivel Eye Bolt |
Rigging and Hanging Equipment |
| Marine Eye Bolt |
Marine Environments and Outdoor Applications |
| Drop Forged Eye Bolt |
Construction and Industrial Uses |
| Lag Eye Bolt |
Wooden Structures or Beams, Often Used in Carpentry and Woodworking |
| Metric Eye Bolt |
Required When Metric Measurements Are Needed |
| Safety Eye Bolt |
Critical Safety Applications, Such as in Safety Rigging |
| Rigging Eye Bolt |
Used in Lifting and Hoisting Operations |
Refer T-head Bolts Standard and Threads
T-Head Bolts, also known as Hammer-Head Bolts, feature a distinctive "T" shaped head that facilitates easy insertion into slots while preventing rotation during installation. Adhering to specific standards ensures these bolts meet desired dimensions, strength, and features to handle intended weights and pressures effectively, minimizing the risk of failures and costly repairs.
Dimensional Standards of T-Head Bolts
| ITEM DESCRIPTION |
HEX SOCKET HEAD SCREW/ALLEN BOLT |
| ITEM TYPE |
FULL THREAD |
HALF/PARTIAL THREADED |
| INCH SERIES |
ASME |
ASME B18.3 |
| METRIC SERIES |
ASME |
ASME B18.3.1M |
| DIN/ISO |
ISO 4762 |
| IS |
IS 2269 |
Tolerance Standards for Concrete of T-Head Bolts
| FEATURE |
THREAD FIT |
LENGTH |
THREAD LENGTH |
| ITEM TYPE |
FULL/HALF/PARTIAL THREAD |
FULL/HALF/PARTIAL THREAD |
HALF/PARTIAL THREAD |
| INCH SERIES |
ASME |
ASME B 1.1- Cl 2A |
ASME B 1.1- Cl 3A |
ASME B18.3 |
ASME B18.3 |
| METRIC SERIES |
ASME |
ASME B 1.13M-6g |
– |
– |
| DIN/ISO |
ISO 724, ISO 965-1 – 6g |
DIN ISO 965-1 – 6g |
ISO 4762 |
ISO 4762 |
| IS |
IS 4218 PART VI -6g |
IS 2269 |
IS 2269 |
J Anchor Bolts Are Widely Used to Secure Walls to Concrete
J Anchor Bolts are available in a variety of sizes, finishes, and materials to cater to diverse requirements. They serve as excellent fasteners for anchoring structural components to concrete, commonly used in manufacturing and durable applications. Installation is relatively straightforward compared to other anchoring methods, and they can be easily removed and replaced without significantly affecting neighboring materials, allowing for modifications within the application.
Types of J Bolts
- Standard J Bolt
- Heavy-Duty J Bolt
- L-Shaped J Bolt
- Corrosion-Resistant J Bolt
- Anchor J Bolt
- Threaded J Bolt
- Lag J Bolt
- Metric J Bolt
- Custom J Bolt
Uses of J Anchor Bolts
| Application |
Uses |
| Construction |
Stabilizing structural structures by fastening columns, beams, and posts to concrete foundations. |
| Structural Support |
Bridges, Buildings, and Industrial Frameworks. |
| Foundation Anchoring |
Anchoring fence posts, support beams, and vertical structures to foundations. |
| Industrial Applications |
Mounting machinery and securing heavy industrial components. |
| Marine Applications |
Anchoring docks, marine equipment. |
| Outdoor and Landscaping |
Securing garden structures, outdoor furniture, and fixtures. |
| Agricultural Uses |
Securing irrigation systems and stabilizing agricultural equipment. |
Hex Head Anchor Bolt Interior Uses




