Table of contents
What is Seamless Tube
What is Welded Tubes
Pressure Capacity of Seamless And Welded Tubing
Seamless vs Welded Tubing
Difference Between ERW and Seamless Tube Price
Advantages and Disadvantages of seamless and welded tube
Seamless Tubing Sizes
Seamless Steel Tubes Manufacturing Process
Welded Steel Tube Manufacturing Process
Seamless Tubing vs DOM Tubing
Seamless Steel Tube Uses
Application for Welded Round Tubing
Mechanical Properties of ERW vs Seamless Tube
Finish for Welded and Seamless Tubes
Seamless Tube Weight Chart
SMLS Tube Extrusion Process
Welded Tube Types
Seamless tubes are designed to withstand higher pressure than welded tubes
One of the key advantages of seamless tubes is that they do not have a weld seam, which makes them more resistant to stress and potential failure points. This feature allows them to handle higher pressure applications with greater reliability. Below is a detailed comparison of the pressure ratings for both types of tubes.
Pressure Capacity of Seamless And Welded Tubing
Welded tubes often have larger diameters and thinner walls
This design makes them ideal for architectural and construction applications where precise dimensions are needed. Because they can be manufactured more quickly, they are also easier to customize for specific projects. As a result, you can achieve larger diameters and thinner walls tailored to your unique requirements.
Seamless vs Welded Tubing
Description
Seamless Tubing
Welded Tubing
Manufacturing Process
Seamless tubes are made from a solid billet that is heated and extruded into a tubular shape without any weld seams.
Formed from flat metal strips that are rolled and welded along their length.
Length
Shorter in length
Available in long continuous lengths
Strength
Stronger
Lower compared to seamless
Uniformity
More uniform wall thickness
Wall thickness may vary slightly
Applications
Used for high-pressure applications and critical structural components.
Commonly used in less critical applications
Corrosion Resistance
More corrosion-resistant.
Less corrosion resistance.
Cost
More expensive
Less expensive
Manufacturing Flexibility
Less flexible
More flexible
Surface Quality
Rough because of extrusion process
Smooth high-quality surface
Surface Finish
Smoother finish and few surface defects.
Surface finish can be less consistent due to the welding process
Ovality
Provide better ovality and roundness
 Poor ovality and roundness
Inspection & Testing
Requires more rigorous testing to ensure quality and strength.
May require less rigorous testing
Internal surface check
Not possible
Checked before manufacturing
Size Range
Available in a more limited range of sizes than welded tubing.
Can be produced in a large range of sizes and lengths.
Welded tubing is generally less expensive than seamless tubing
The production of welded tubes is faster and more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for industries that require low to medium pressure applications. The lower cost is also due to reduced labor and material expenses during the manufacturing process.
Difference Between ERW and Seamless Tube Price
Seamless Tube
ERW Steel Tube
More expensive : can be 1.5 to 3 times the cost of welded tubes
Less expensive : more affordable by 30% to 60% compared to seamless tubes
Factor affecting : Manufacturing Process, Quality, Production Costs, Demand
Advantages and Disadvantages of seamless and welded tube
The Pros and Cons of Hot Finished Seamless Type Tubes
Pros
Cons
Excellent corrosion resistance
Expensive
Good Durability
Difficult to manufacture
High pressure rating
Not ideal for thin wall large diameter tubes
Good Purity
Longer lead times
Ideal for critical applications
Â
The Pros and Cons of Welded Tubes
Pros
Cons
Better lead times
Suitable for Heavy wall applications
Less Expensive
Less corrosion resistant
Available in long lengths
Slight impurities
Thinner wall
Stress concentration
More consistent concentricity
Â
Tighter tolerances
Â
Seamless Tubing Sizes
NPS
Schedule
DN
OD
Wall thck
Weight
[inch]
[inch]
[lbs/ft]
1/8
10
6
.405
.049
.19
Â
40
Â
Â
.068
.24
Â
80
Â
Â
.095
.31
1/4
10
8
.54
.065
.33
Â
40
Â
Â
.088
.42
Â
80
Â
Â
.119
.54
3/8
10
10
.675
.065
.42
Â
40
Â
Â
.091
.57
Â
80
Â
Â
.126
.74
1/2
5
15
.84
.065
.54
Â
30
Â
Â
.095
.76
Â
40
Â
Â
.109
.85
Â
160
Â
Â
.188
1.31
3/4
5
20
1.05
.065
.69
Â
30
Â
Â
.095
.97
Â
80
Â
Â
.154
1.47
Â
160
Â
Â
.219
1.94
1
5
25
1.315
.065
.87
Â
10
Â
Â
.109
1.41
Â
40
Â
Â
.133
1.68
Â
160
Â
Â
.25
2.84
1 1/4
5
32
1.66
.065
1.11
Â
30
Â
Â
.117
1.93
Â
80
Â
Â
.191
3
Â
160
Â
Â
.25
3.76
1 1/2
5
40
1.9
.065
1.28
Â
10
Â
Â
.109
2.09
Â
40
Â
Â
.145
2.72
Â
80
Â
Â
.2
3.63
Â
160
Â
Â
.281
4.86
2
5
50
2.375
.065
1.61
Â
Â
Â
Â
.109
2.64
Â
Â
Â
Â
.141
3.36
Â
40
Â
Â
.154
3.65
Â
Â
Â
Â
.188
4.39
Â
80
Â
Â
.218
5.02
Â
Â
Â
Â
.281
6.28
Â
160
Â
Â
.344
7.46
2 1/2
5
65
2.875
.038
2.47
Â
10
Â
Â
.12
3,53
Â
Â
Â
Â
.125
3.67
Â
Â
Â
Â
.156
4.53
Â
Â
Â
Â
.188
5.4
Â
40
Â
Â
.203
5.79
Â
80
Â
Â
.276
7.66
Â
160
Â
Â
.375
1 .01
3
Â
80
3.5
.083
3.03
Â
10
Â
Â
.12
4,34
Â
Â
Â
Â
.141
5.06
Â
Â
Â
Â
.172
6.11
Â
40
Â
Â
.216
7.58
Â
Â
Â
Â
.281
9.66
Â
80
Â
Â
.3
1 .25
Â
160
Â
Â
.438
14.32
3 1/2
5
90
4
.083
3.48
Â
10
Â
Â
.12
4.98
Â
Â
Â
Â
.141
5.81
Â
Â
Â
Â
.172
7.03
Â
40
Â
Â
.226
9.11
Â
Â
Â
Â
.281
11.16
Â
80
Â
Â
.318
12.5
4
5
100
4.5
.083
3.92
Â
10
Â
Â
.12
5.62
Â
Â
Â
Â
.141
6.56
Â
Â
Â
Â
.172
7.95
Â
Â
Â
Â
.203
9.32
Â
40
Â
Â
.237
1 .79
Â
Â
Â
Â
.281
12.66
Â
80
Â
Â
.337
14.98
Â
160
Â
Â
.531
22.51
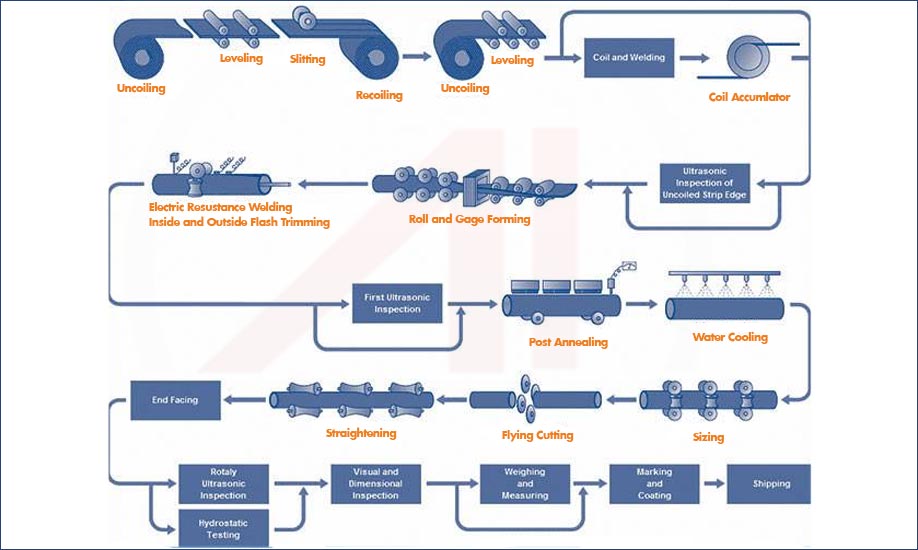
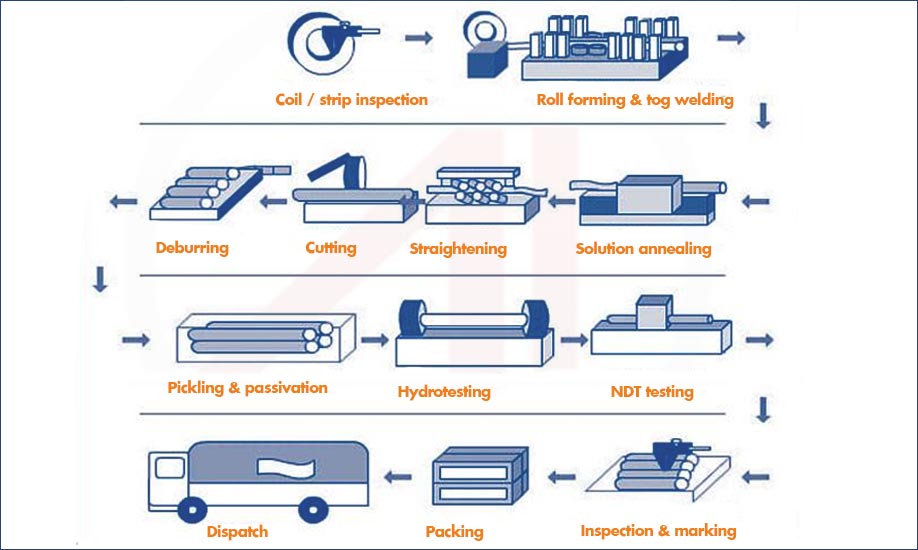
Seamless steel tube is extruded and drawn from a billet while welded tube is manufactured from a strip
The difference between the two tubes lies in their manufacturing processes. Seamless tubes do not have any weld seams, which gives them higher strength and makes them suitable for high-pressure conditions. In contrast, welded tubes have welds, which can reduce their strength and make them more appropriate for applications with medium to low pressure conditions.
Seamless Steel Tubes Manufacturing Process
Welded Steel Tube Manufacturing Process
Seamless Tubing vs DOM Tubing
Description
Seamless Tube
DOM Tubing
Manufacturing Process
Made from a solid billet
Starts as a welded tube, then drawn over a mandrel
Advantages
High strength and durability
Good dimensional accuracy
Strength
Higher
Improved strength compared to standard welded tubes, but not as stronger than seamless tubing
Weld Seams
No weld seams
Originally welded, but weld seam is removed during the mandrel process
Dimensional Accuracy
High
Very high
Surface Finish
Varies
smooth and uniform after mandrel drawing
Cost
More
Less
Seamless Steel Tube Uses
Aerospace
Oil and gas
Structural components in demanding environments
High-pressure hydraulic systems
Seamless annealed tubing is more expensive than welded round tubing
Seamless annealed tubing goes through multiple processes, which increases its cost. These processes take longer and involve higher labor and machining costs, making seamless tubing more expensive than welded tubing.
Application for Welded Round Tubing
General structural applications
Piping and tubing in less demanding environments
Automotive components
Furniture and general manufacturing
Mechanical Properties of ERW vs Seamless Tube
Property
Seamless Tubes
ERW Steel Tubes
Tensile Strength
Higher than welded
Lower than seamless
Yield Strength
Consistent across the entire tube
May vary
Elongation
Better
Can be reduced at the weld seam and heat-affected zones – HAZ
Impact Toughness
Higher
Lower
Fatigue Resistance
Higher
Lower
Hardness
Typically more consistent throughout the tube.
Show variation
Weld Integrity
N/A
Quality of the weld can impact overall mechanical properties
Finish for Welded and Seamless Tubes
Seamless tubing
Cold Drawn Finish
Hot Finished
Polishing
Passivation
Coating
Welded tubing
Heat Treatment
Descaling
Polishing
Coating
Anodizing
Seamless Tube Weight Chart
Nominal Tube Size
inch
1/8
1/4
3/8
1/2
3/4
1
1.1/4
1.1/2
2
2.1/2
3
4
5
6
8
10
12
mm
3
6
10
15
20
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
150
200
250
300
Outside Diameter
mm
10.3
13.7
17.1
21.3
26.7
33.4
42.2
48.3
60.3
73
88.9
114.3
141.3
168.3
219.1
273.1
323.8
Sched 5 S
Weight in kgm
0.2
0.37
0.47
0.8
1.03
1.3
1.65
1.91
2.4
3.69
4.51
5.84
9.47
11.32
14.79
22.63
31.25
WT in mm
1.2
1.2
1.2
1.65
1.65
1.65
1.65
1.65
1.65
2.11
2.11
2.11
2.77
2.77
2.77
3.4
3.96
Sched 10 S
Weight in kgm
0.28
0.49
0.63
1
1.28
2.09
2.7
3.11
3.93
5.26
6.45
8.36
11.57
13.84
19.96
27.78
36
WT in mm
1.24
1.65
1.65
2.11
2.11
2.77
2.77
2.77
2.77
3.05
3.05
3.05
3.4
3.4
3.76
4.19
4.57
Sched 20 S
Weight in kgm
0.33
0.58
0.74
1.07
1.52
1.94
2.9
3.55
4.24
6.81
8.37
12.18
16.8
25.36
33.31
41.77
49.7
WT in mm
1.5
2
2
2.3
2.55
2.55
3
3
3
4
4
4.5
5
6.35
Interlock Bottom Bracket
· PREMIUM QUALITY: Precision machining, with high quality assurance of comprehensive performance.
· HIGH RELIABILITY: Professional manufacturing, stable characteristics and high reliability.
· HIGH QUALITY MATERIAL: Made of high quality alloy material, sturdy, durable and long service life.
· MORE CONVENIENT: Simple design, easy to install and operate, convenient to use.
· STURDY AND DURABLE: The special design of the threaded bottom bracket, where the cups are threaded and screwed together within frame, ensures avoid any squeaking.
Interlock Bottom Bracket,Aluminum Cup Bottom Brackets,Press Fit Bottom Bracket,Bicycle Child
Shenzhen Gineyea Technology Co., LTD. , https://www.gineyea.com
Post navigation